How To Start Ftp Service On Rhel7
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a traditional and widely used standard tool for transferring files betwixt a server and clients over a network, peculiarly where no authentication is necessary (permits bearding users to connect to a server). We must understand that FTP is unsecure by default, because it transmits user credentials and data without encryption.
In this guide, we volition depict the steps to install, configure and secure a FTP server (VSFTPD stands for "Very Secure FTP Daemon") in CentOS/RHEL 7 and Fedora distributions.
Annotation that all the commands in this guide will be run as root, in case you are non operating the server with the root account, use the sudo command to proceeds root privileges.
Step i: Installing FTP Server
ane. Installing vsftpd server is straight forward, simply run the post-obit command in the concluding.
# yum install vsftpd
ii. After the installation completes, the service will be disabled at first, so nosotros need to start it manually for the fourth dimension being and enable it to start automatically from the next system boot as well:
# systemctl start vsftpd # systemctl enable vsftpd
iii. Next, in order to permit admission to FTP services from external systems, we accept to open port 21, where the FTP daemons are listening every bit follows:
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=21/tcp # firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add together-service=ftp # firewall-cmd --reload
Step 2: Configuring FTP Server
4. At present nosotros will motility over to perform a few configurations to setup and secure our FTP server, allow us start by making a backup of the original config file /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf:
# cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.orig
Side by side, open up the config file in a higher place and set the following options with these corresponding values:
anonymous_enable=NO # disable anonymous login local_enable=Aye # let local logins write_enable=YES # enable FTP commands which change the filesystem local_umask=022 # value of umask for file cosmos for local users dirmessage_enable=YES # enable showing of messages when users first enter a new directory xferlog_enable=Yes # a log file will be maintained detailing uploads and downloads connect_from_port_20=YES # utilize port 20 (ftp-information) on the server motorcar for PORT mode connections xferlog_std_format=Yes # go on standard log file format listen=NO # forbid vsftpd from running in standalone mode listen_ipv6=Yes # vsftpd will listen on an IPv6 socket instead of an IPv4 1 pam_service_name=vsftpd # proper name of the PAM service vsftpd will use userlist_enable=YES # enable vsftpd to load a listing of usernames tcp_wrappers=YES # turn on tcp wrappers
5. Now configure FTP to permit/deny FTP access to users based on the user list file /etc/vsftpd.userlist.
Past default, users listed in userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist are denied login access with userlist_deny option set to YES, if userlist_enable=YES.
All the same, userlist_deny=NO alters the setting, meaning that simply users explicitly listed in userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist will be permitted to login.
userlist_enable=YES # vsftpd will load a listing of usernames, from the filename given by userlist_file userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd.userlist # stores usernames. userlist_deny=NO
That's not all, when users login to the FTP server, they are placed in a chroot'ed jail, this is the local root directory which will act as their dwelling house directory for the FTP session only.
Next, nosotros will look at two possible scenarios of how to chroot FTP users to Dwelling directories (local root) directory for FTP users, as explained below.
six. Now add these two following options to restrict FTP users to their Home directories.
chroot_local_user=Yep allow_writeable_chroot=YES
chroot_local_user=Yeah means local users will be placed in a chroot jail, their dwelling house directory afterward login past default settings.
And also past default, vsftpd does not allow the chroot jail directory to be writable for security reasons, however, we tin use the option allow_writeable_chroot=Yes to override this setting.
Save the file and close it.
Securing FTP Server with SELinux
seven. Now, let's prepare the SELinux boolean beneath to allow FTP to read files in a user's home directory. Note that this was initially done using the the command:
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
Notwithstanding, the ftp_home_dir directive has been disabled past default as explained in this bug report: https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1097775.
Now we will use semanage command to ready SELinux dominion to let FTP to read/write user's domicile directory.
# semanage boolean -chiliad ftpd_full_access --on
At this bespeak, we accept to restart vsftpd to effect all the changes we made so far to a higher place:
# systemctl restart vsftpd
Step 4: Testing FTP Server
viii. Now we volition exam FTP server by creating a FTP user with useradd command.
# useradd -chiliad -c "Ravi Saive, CEO" -s /bin/bash ravi # passwd ravi
Afterwards, we take to add the user ravi to the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist using the echo control as follows:
# repeat "ravi" | tee -a /etc/vsftpd.userlist # cat /etc/vsftpd.userlist
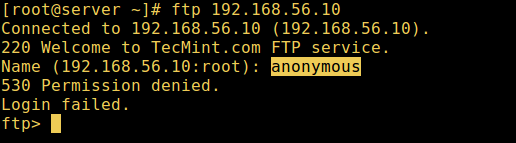
9. Now it's time to test if our settings above are working correctly. Let'southward start by testing anonymous logins, we can see from the screen shot below that anonymous logins are not permitted:
# ftp 192.168.56.10 Continued to 192.168.56.x (192.168.56.10). 220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service. Name (192.168.56.x:root) : anonymous 530 Permission denied. Login failed. ftp>
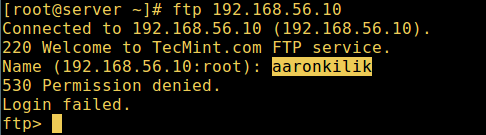
10. Allow's also test if a user not listed in the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist will be granted permission to login, which is not the case equally in the screen shot beneath:
# ftp 192.168.56.10 Connected to 192.168.56.x (192.168.56.ten). 220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service. Proper name (192.168.56.x:root) : aaronkilik 530 Permission denied. Login failed. ftp>
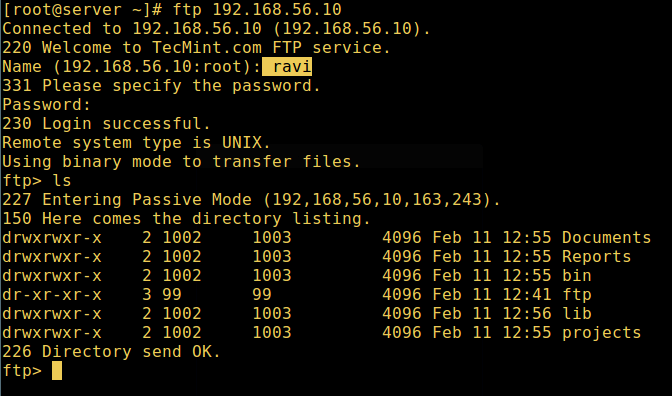
11. Now practice a final cheque if a user listed in the file /etc/vsftpd.userlist, is actually placed in his/her habitation directory after login:
# ftp 192.168.56.10 Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.10). 220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service. Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi 331 Please specify the countersign. Password: 230 Login successful. Remote organization blazon is UNIX. Using binary mode to transfer files. ftp> ls
Warning: Using allow_writeable_chroot=YES has sure security implications, especially if the users have upload permission, or trounce access.
Only activate this option if y'all exactly know what you are doing. It's of import to note that these security implications arenot vsftpd specific, they apply to all FTP daemons which offer to put local users in chroot jails as well.
Therefore, we will look at a more secure way of setting a unlike non-writable local root directory in the adjacent section.
Step 5: Configure Different FTP User Home Directories
12. Open the vsftpd configuration file once again and get-go by commenting the unsecure option below:
#allow_writeable_chroot=Yes
Then create the alternative local root directory for the user (ravi, yours is probably different) and remove write permissions to all users to this directory:
# mkdir /domicile/ravi/ftp # chown nobody:nobody /abode/ravi/ftp # chmod a-w /home/ravi/ftp
13. Side by side, create a directory nether the local root where the user will store his/her files:
# mkdir /home/ravi/ftp/files # chown ravi:ravi /home/ravi/ftp/files # chmod 0700 /home/ravi/ftp/files/
So add/modify the following options in the vsftpd config file with these values:
user_sub_token=$USER # inserts the username in the local root directory local_root=/abode/$USER/ftp # defines any users local root directory
Save the file and close it. Once over again, let's restart the service with the new settings:
# systemctl restart vsftpd
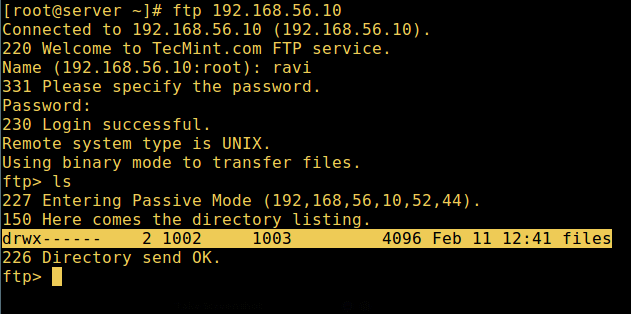
fourteen. At present exercise a concluding examination again and encounter that the users local root directory is the FTP directory nosotros created in his abode directory.
# ftp 192.168.56.x Connected to 192.168.56.10 (192.168.56.x). 220 Welcome to TecMint.com FTP service. Name (192.168.56.10:root) : ravi 331 Please specify the password. Password: 230 Login successful. Remote system type is UNIX. Using binary mode to transfer files. ftp> ls
That's it! In this article, we described how to install, configure as well as secure a FTP server in CentOS 7, use the comment section below to write dorsum to us concerning this guide/share whatever useful data near this topic.
Suggested Read: Install ProFTPD Server on RHEL/CentOS 7
In the next article, nosotros volition also testify you how to secure an FTP server using SSL/TLS connections in CentOS vii, until then, stay connected to TecMint.
How To Start Ftp Service On Rhel7,
Source: https://www.tecmint.com/install-ftp-server-in-centos-7/
Posted by: fosterretion1985.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Start Ftp Service On Rhel7"
Post a Comment